(a) Using bond-dissociation energies (Table 5.6), which of the indicated bonds should break most easily?
(b) How does that help you explain the results shown in Figure 11.40?

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: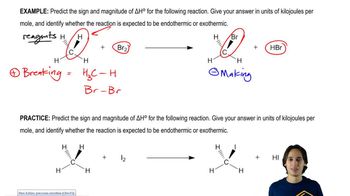


 4:09m
4:09mMaster How to calculate enthalpy using bond dissociation energies. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning