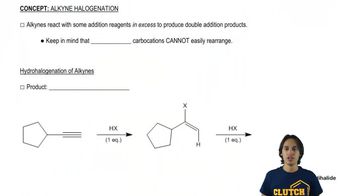
Suggest reagents you might use to generate the product from the given reactant.
(b)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:


 4:19m
4:19mMaster Understanding how to convert terminal alkynes to alkynides. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning