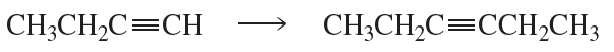Show how you might synthesize the following compounds, using acetylene and any suitable alkyl halides as your starting materials. If the compound given cannot be synthesized by this method, explain why.
d. 4-methylhex-2-yne
e. 5-methylhex-2-yne
f. cyclodecyne