Show the products of the following acetylide alkylation reactions. [Make sure your product has the correct number of carbons.]
(b)

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: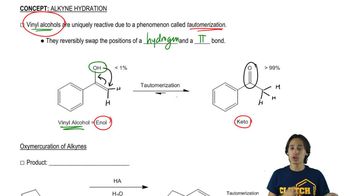
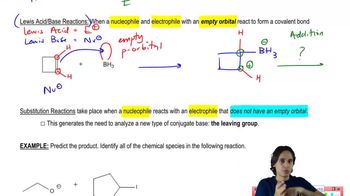


 4:19m
4:19mMaster Understanding how to convert terminal alkynes to alkynides. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning