Textbook Question
For each molecular formula, draw all the isomeric alkynes, and give their IUPAC names. Circle the acetylenic hydrogen of each terminal alkyne.
(b) C6H10 (seven isomers)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: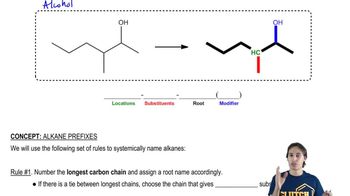

 3:43m
3:43mMaster The different parts of an IUPAC name with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning