Textbook Question
Phenylacetone can form two different enols.
(c) Propose mechanisms for the formation of the second enol in acid.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: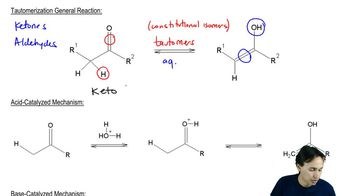
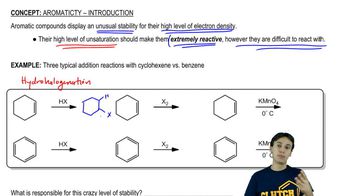
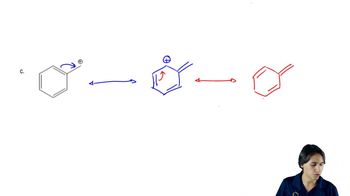

 1:51m
1:51mMaster Unusual Acidity of the Alpha Carbon with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning