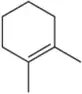
Predict the major products of the following reactions, and give the structures of any intermediates. Include stereochemistry where appropriate.
(j)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: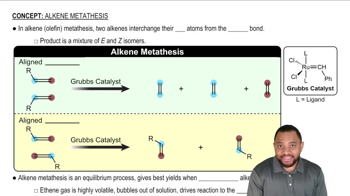
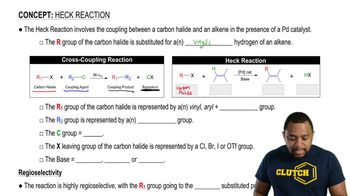
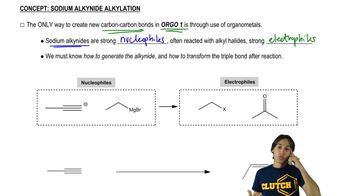

 3:50m
3:50mMaster General properties of syn vicinal dihydroxylation. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning