Predict the product(s) that would result when the alkenes are allowed to react under the following conditions: (vi) 1. OsO4 2. NaHSO3
(h)
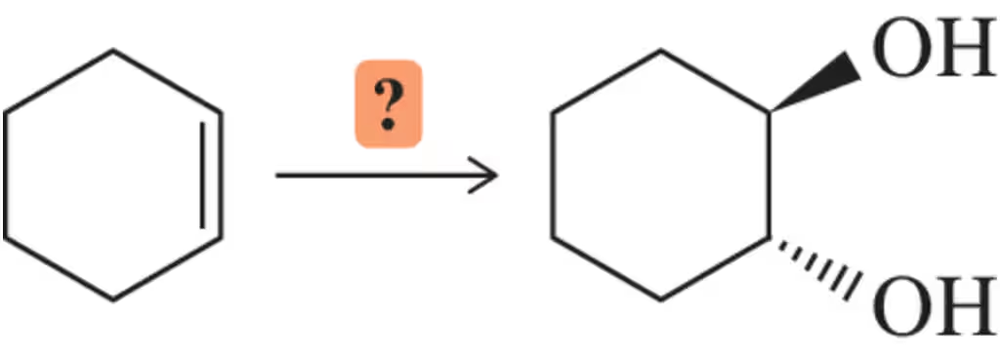
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:

 3:50m
3:50mMaster General properties of syn vicinal dihydroxylation. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning