Draw the structure for each of the following:
c. ethyl vinyl ether
d. allyl alcohol
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: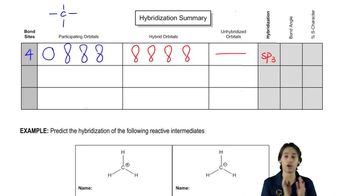
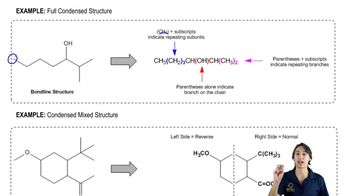


 6:06m
6:06mMaster How to interpret condensed structures. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning