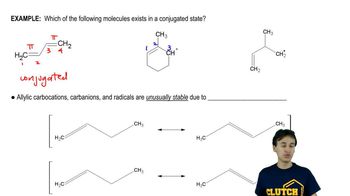
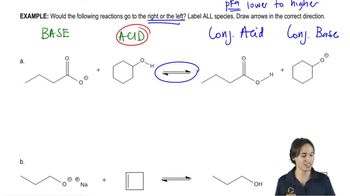
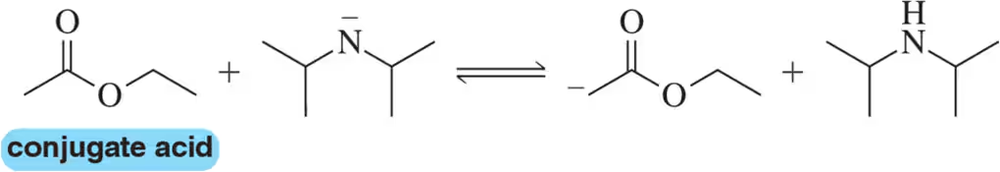Write the equation that shows how a buffer made by dissolving CH3COOH and CH3COO−Na+ in water prevents the pH of a solution from changing appreciably when
a. a small amount of H+ is added to the solution.
b. a small amount of HO− is added to the solution.