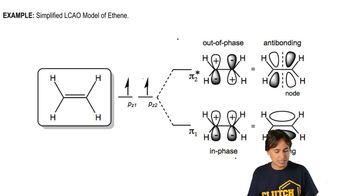
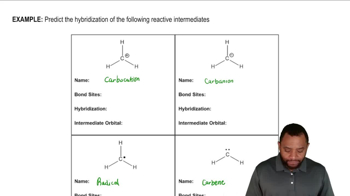
Indicate the kind of molecular orbital (σ, σ*, π, or π*) that results when the two atomic orbitals are combined:
a. <IMAGE>
b. <IMAGE>
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:

 2:19m
2:19mMaster What’s the difference between sigma and pi bonds? with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning