A student was given the structural formulas of several compounds and was asked to give them systematic names. How many did the student name correctly? Correct those that are misnamed.
g. 3,3-dichlorooctane
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: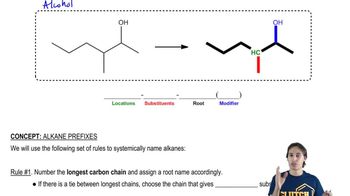

 3:43m
3:43mMaster The different parts of an IUPAC name with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning