Textbook Question
Give IUPAC names for the following compounds.
(g)
(h)
(i)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: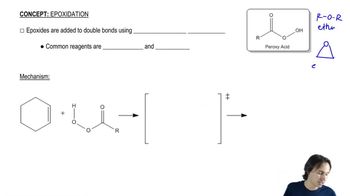



 1:09m
1:09mMaster Defining what an epoxide (oxirane) is. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning