Predict the product(s) you would expect from treatment of each compound with (1) dilute, neutral KMnO4 and (2) warm basic KMnO4, then dilute acid.
(e) cyclodecyne
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: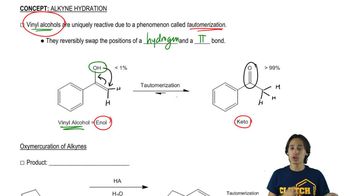
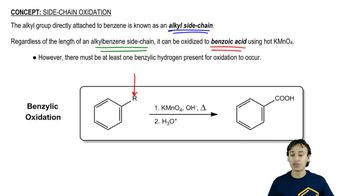
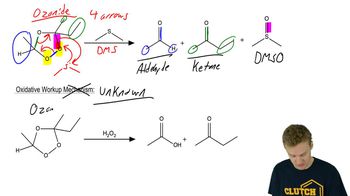

 2:13m
2:13mMaster General features of alkyne cleavage. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning