Oxidative cleavages can help to determine the positions of the triple bonds in alkynes.
(b) An unknown alkyne undergoes oxidative cleavage to give the following triacid plus one equivalent of propionic acid. Propose a structure for the alkyne.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: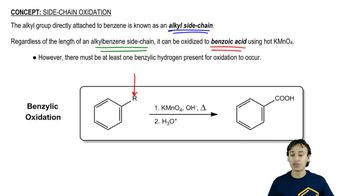

 2:13m
2:13mMaster General features of alkyne cleavage. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning