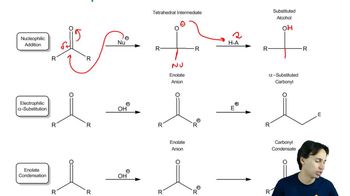
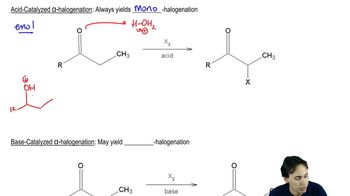
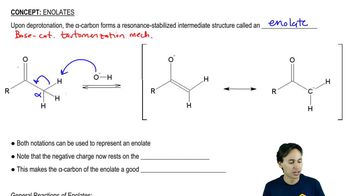
Heating an alcohol with sulfuric acid is a good way to prepare a symmetrical ether such as diethyl ether.
a. Explain why it is not a good way to prepare an unsymmetrical ether such as ethyl propyl ether.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: