Multiple Choice
What type of intermolecular force is likely to occur between two water molecules or strands of DNA?
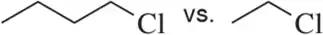
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: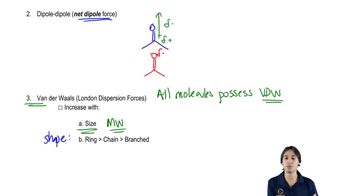


 3:08m
3:08mMaster How IMFs are related to melting and boiling points. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning