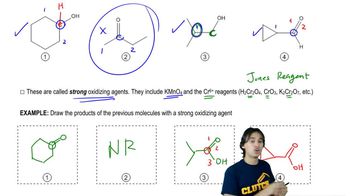
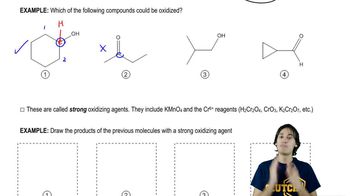
Which of the following compounds would give a positive Tollens test? (Remember that the Tollens test involves mild basic aqueous conditions.)
(d) CH3CH2CH2CH2CH(OH)OCH3
(e) CH3CH2CH2CH2CH(OCH3)2
(f)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: