Draw the structures of the compound ethyl β-D-ribofuranoside.
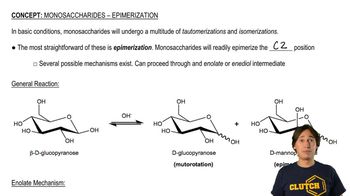
Allose is the C3 epimer of glucose, and ribose is the C2 epimer of arabinose.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:

 6:23m
6:23mMaster Monosaccharides - Forming Cyclic Hemiacetals with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning