Classify each hydrogen atom in the following compounds as primary (1°), secondary (2°), or tertiary (3°).
a. butane
b. isobutane
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: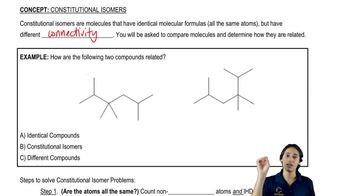

 6:42m
6:42mMaster Understanding Non-IUPAC Substituents with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning