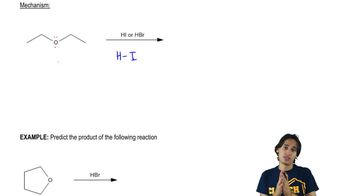
b. A small amount of a product containing a six-membered ring is also formed. Draw the structure of that product.
c. Why is so little six-membered ring product formed?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:


 4:34m
4:34mMaster Acid-Catalyzed Epoxide Ring-Opening with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning