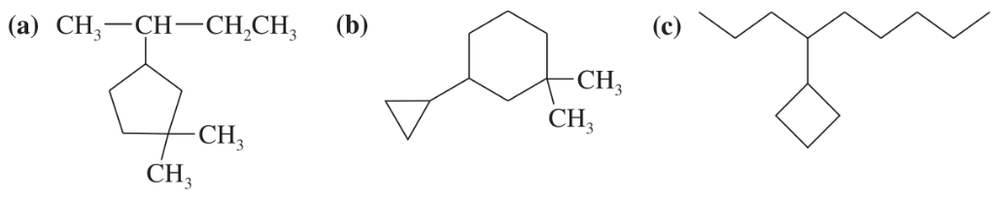
Name the following cycloalkanes using the IUPAC system of nomenclature. [Hint: Each molecule exemplifies one of the cycloalkane nomenclature rules in Table 3.10.]
(a) rule 1
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:


 1:11m
1:11mMaster How to find the root name for cycloalkanes with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning