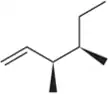
Give the expected major product for each reaction, including stereochemistry where applicable.
(a) but-1-ene + H2/Pt
(b) cis-but-2-ene + H2/Ni
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:

 5:21m
5:21mMaster General properties of catalytic hydrogenation. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning