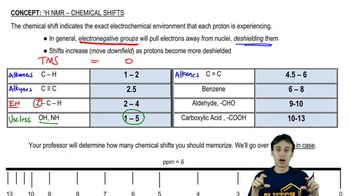
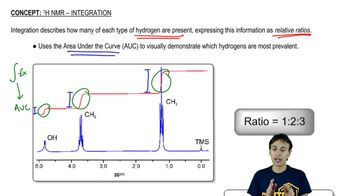
How many signals would you expect to see in the 1H NMR spectrum of each of the following compounds?
g.
h.
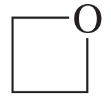
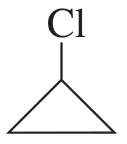
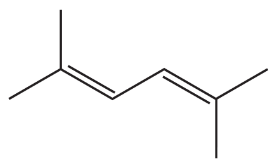
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:

 4:35m
4:35mMaster General Assumption for 1H NMR Signals with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning