A compound gives the following IR spectrum. Upon reaction with sodium borohydride followed by acidification, it forms the product with the 1H NMR spectrum shown below. Identify the starting material and the product.
<IMAGE>
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: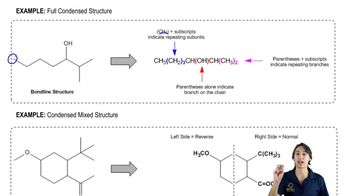
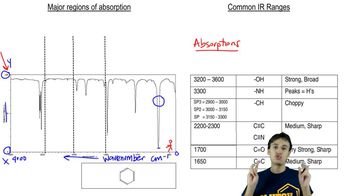
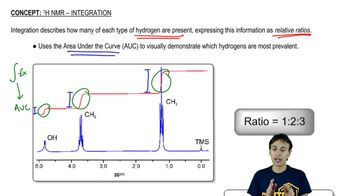

 11:19m
11:19mMaster Building Molecular Sentences with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning