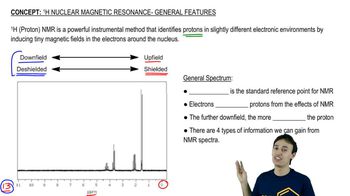
The proton and 13C NMR spectra of a compound of formula C4H11N are shown here. Determine the structure of this amine, and give peak assignments for all of the protons in the structure.
<IMAGE>
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: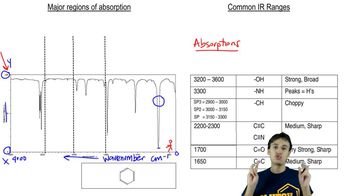

 11:19m
11:19mMaster Building Molecular Sentences with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning