Oxymercuration–reduction, like acid-catalyzed hydration, can be modified to synthesize ethers. Suggest an alkene and the appropriate reaction conditions to synthesize the following ethers.
(a)
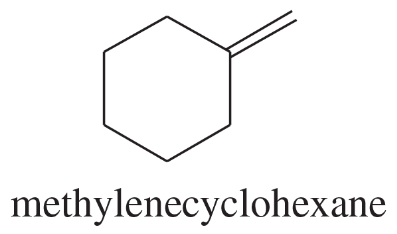
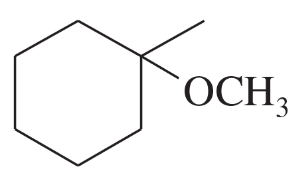
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:


 4:21m
4:21mMaster The Mechanism of Alkoxymercuation. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning