In light of your answer to Assessment 9.47, predict the product of the following reactions we have seen previously where an alcohol is substituted for water.
(b)
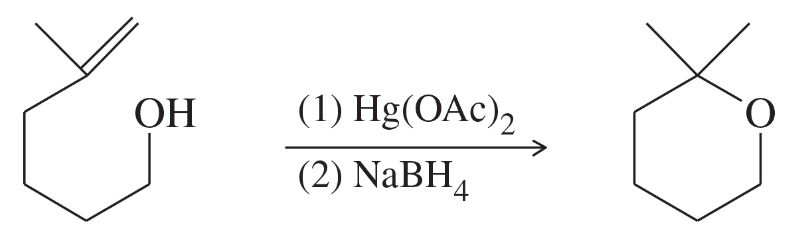
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: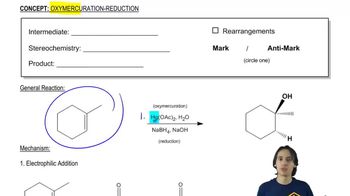


 4:21m
4:21mMaster The Mechanism of Alkoxymercuation. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning