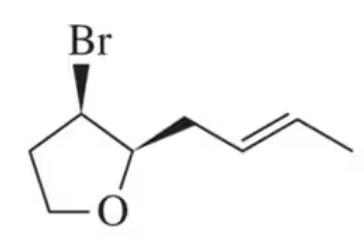
Identify the compound with molecular formula C7H14O that gives the following proton-coupled 13C NMR spectrum:
<IMAGE>
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:


 4:m
4:mMaster 13C NMR General Features with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning