For the molecules in Assessment 15.58, give an approximate chemical shift for each indicated carbon. [The range of correct answers is large here.].
(a)
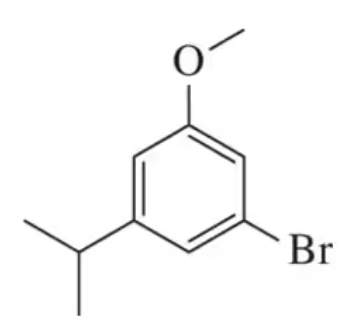
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:


 4:m
4:mMaster 13C NMR General Features with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning