Answer the following questions for each compound:
a. How many signals are in its 13C NMR spectrum?
b. Which signal is at the lowest frequency?
8.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: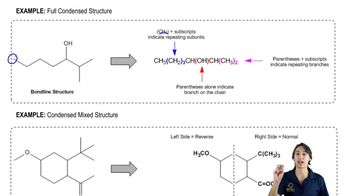



 4:m
4:mMaster 13C NMR General Features with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning