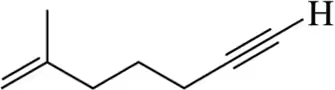
Calculate the number of elements of unsaturation implied by the molecular formula C6H12.
Hint: If you prefer to use a formula, elements of unsaturation = 1/2(2C + 2 - H)
C = number of carbons
H = number of hydrogens
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: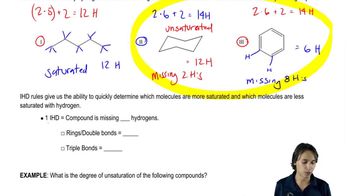


 2:39m
2:39mMaster The difference between saturated and unsaturated molecules. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning