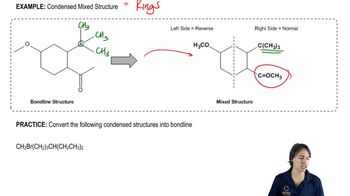
a. What is each compound’s systematic name?
b. Draw a skeletal structure for each condensed structure given and draw a condensed structure for each skeletal structure.
3.
4. (CH3CH2)4C
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: