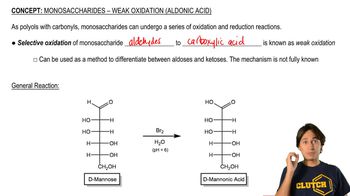
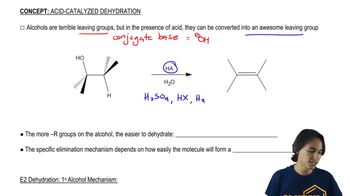
Determine whether the following reactions are redox reactions. If they are, identify whether the molecule has been oxidized or reduced.
(c)
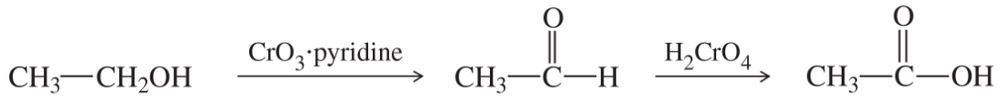
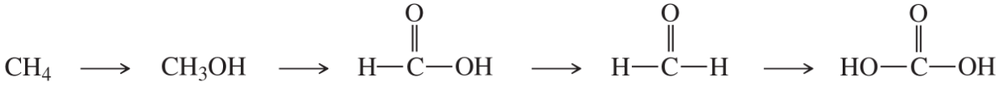
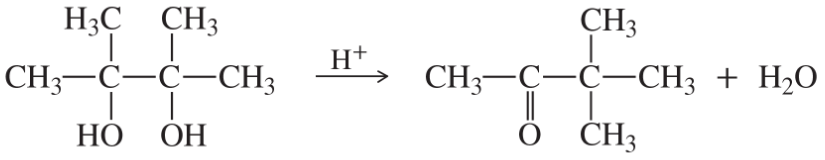
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: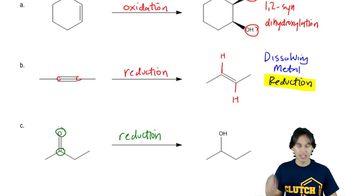

 6:02m
6:02mMaster General Features of Redox with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning