Show how you would accomplish the following multistep syntheses. You may use any additional reagents and solvents you need.
(a) PhCH2CH2OH → PhCH2CH2COOH
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
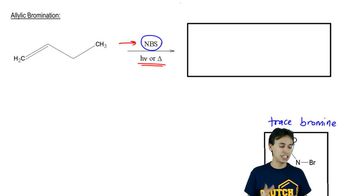

 2:12m
2:12mMaster Carbonation of Grignard Reagents with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning