Show how you would accomplish the following multistep syntheses. You may use any additional reagents and solvents you need.
(b)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: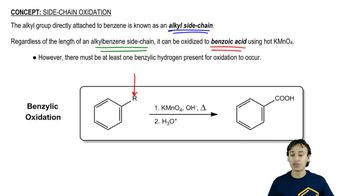



 2:12m
2:12mMaster Carbonation of Grignard Reagents with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning