Identify the electrophile and the nucleophile in each of the following reaction steps and then draw curved arrows to illustrate the bond-making and bondbreaking processes.
a.
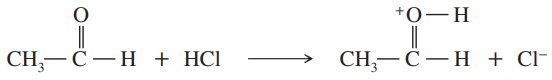
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:

 5:14m
5:14mMaster How to tell if a molecule will be reactive or not. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning