The following reaction steps are shown using conventional electron pushing. (b) Use the bouncing arrow formalism to illustrate the formation of only the product shown.
(a)

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: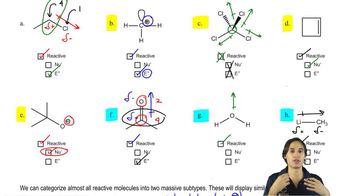

 5:14m
5:14mMaster How to tell if a molecule will be reactive or not. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning