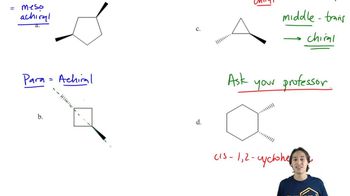
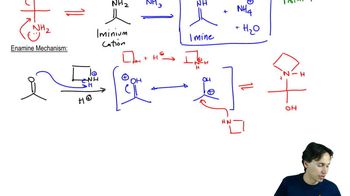
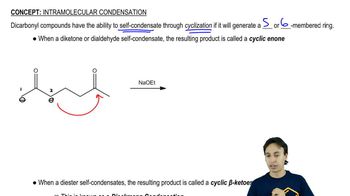
Show how you would accomplish each conversion using an enamine synthesis with pyrrolidine as the secondary amine.
(a) cyclopentanone → 2-allylcyclopentanone
(b) pentan-3-one → 2-methyl-1-phenylpentan-3-one
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: