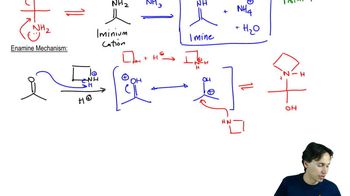
Many of the condensations we have studied are reversible. The reverse reactions are often given the prefix retro-, the Latin word meaning “backward.” Propose mechanisms to account for the following reactions.
(c)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: