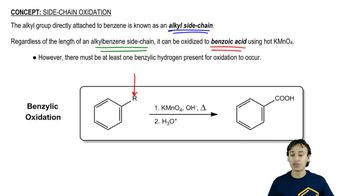
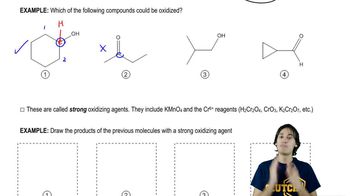
Predict the major products of the following reactions, including stereochemistry where appropriate.
(n) sodium ethoxide + 2-methyl-2-bromobutane
(o) octan-1-ol + DMSO + oxalyl chloride
(p) 4-cyclopentylhexan-1-ol + DMP reagent
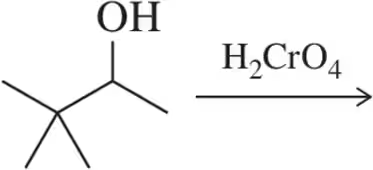
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: