For each of the following pairs of compounds, identify one IR absorption band that could be used to distinguish between them:
i.
j.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: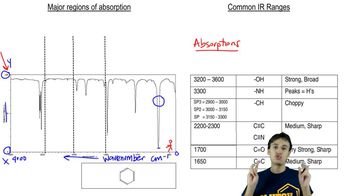


 16:47m
16:47mMaster Common IR Frequencies with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning