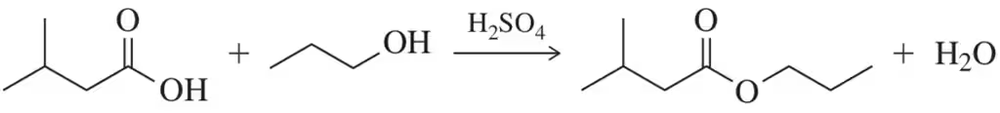
How can IR spectroscopy be used to distinguish between the following compounds?
a. a ketone and an aldehyde
b. a cyclic ketone and an open-chain ketone
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: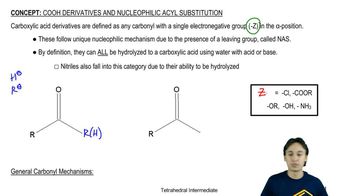
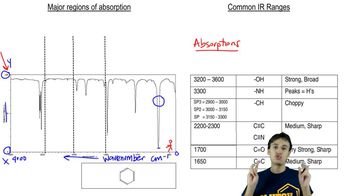
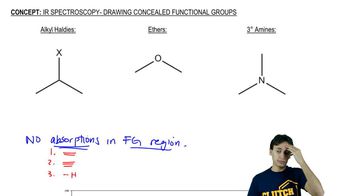

 16:47m
16:47mMaster Common IR Frequencies with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning