Textbook Question
Show all possible constitutional isomers of C5H12O. Label them as functional, positional, or chain isomers.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: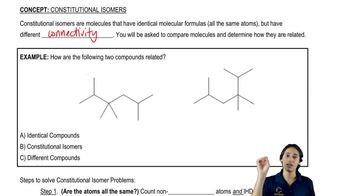


 1:10m
1:10mMaster What is a constitutional isomer? with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning