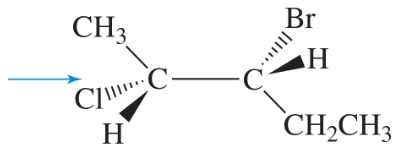
Convert each Newman projection to the equivalent line–angle formula, and assign the IUPAC name. g.
(g)
(h)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:

 0:34m
0:34mMaster Introduction to Drawing Newman Projections with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning