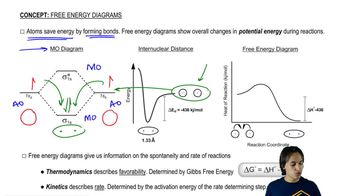
Draw a Newman projection, similar to Figure 3-25 down the C1—C6 bond in the equatorial conformation of methylcyclohexane. Show that the equatorial methyl group is also anti to C5. (Using your models will help.)
<IMAGE>
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: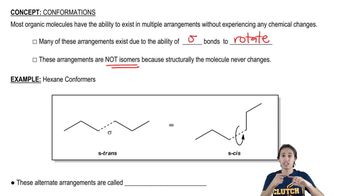


 0:34m
0:34mMaster Introduction to Drawing Newman Projections with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning