Look at the relative positions of each pair of atoms listed here in the periodic table. How many core electrons does each have? How many valence electrons does each have?
a. carbon and silicon
b. oxygen and sulfur
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: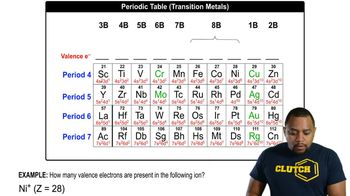


 2:14m
2:14mMaster What is a valence electron? with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning