Using the given starting material, any necessary inorganic reagents, and any carbon-containing compounds with no more than two carbons, indicate how the following syntheses could be carried out:
b.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: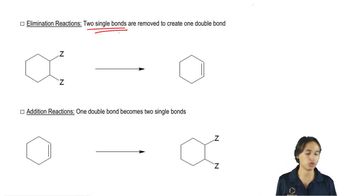
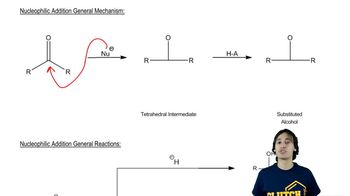
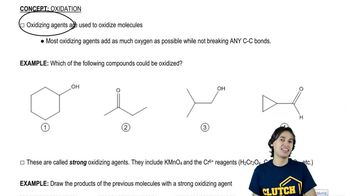

 2:12m
2:12mMaster Carbonation of Grignard Reagents with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning