Show how the following ketones might be synthesized from the indicated acids, using any necessary reagents.
(a) propiophenone from propionic acid (using Friedel–Crafts acylation)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: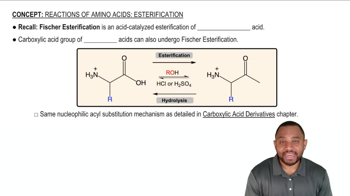


 9:32m
9:32mMaster NAS - The Three Rules with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning