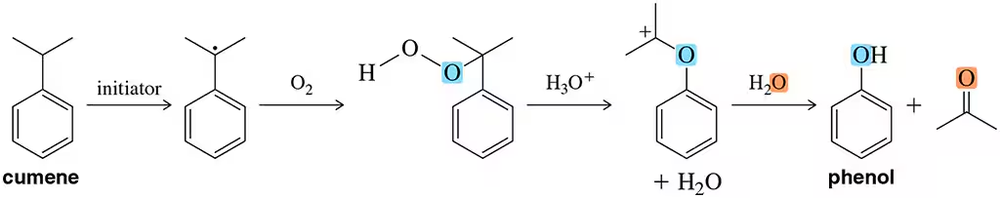
Predict the major products of the following reactions.
(b) phenol + tert-butyl chloride + AlCl3
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:

 2:37m
2:37mMaster Donating vs Withdrawing Groups with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning